After developing your first kidney stone, the probability of developing more in years to come is quite high.
The following article can provide an idea of how to prevent kidney stone recurrence in the future. If you have been through the experience of kidney stones once, the likelihood of you wanting to repeat the process is probably quite slim or nonexistent. Fortunately, there are options to explore that can help prevent stone recurrence.
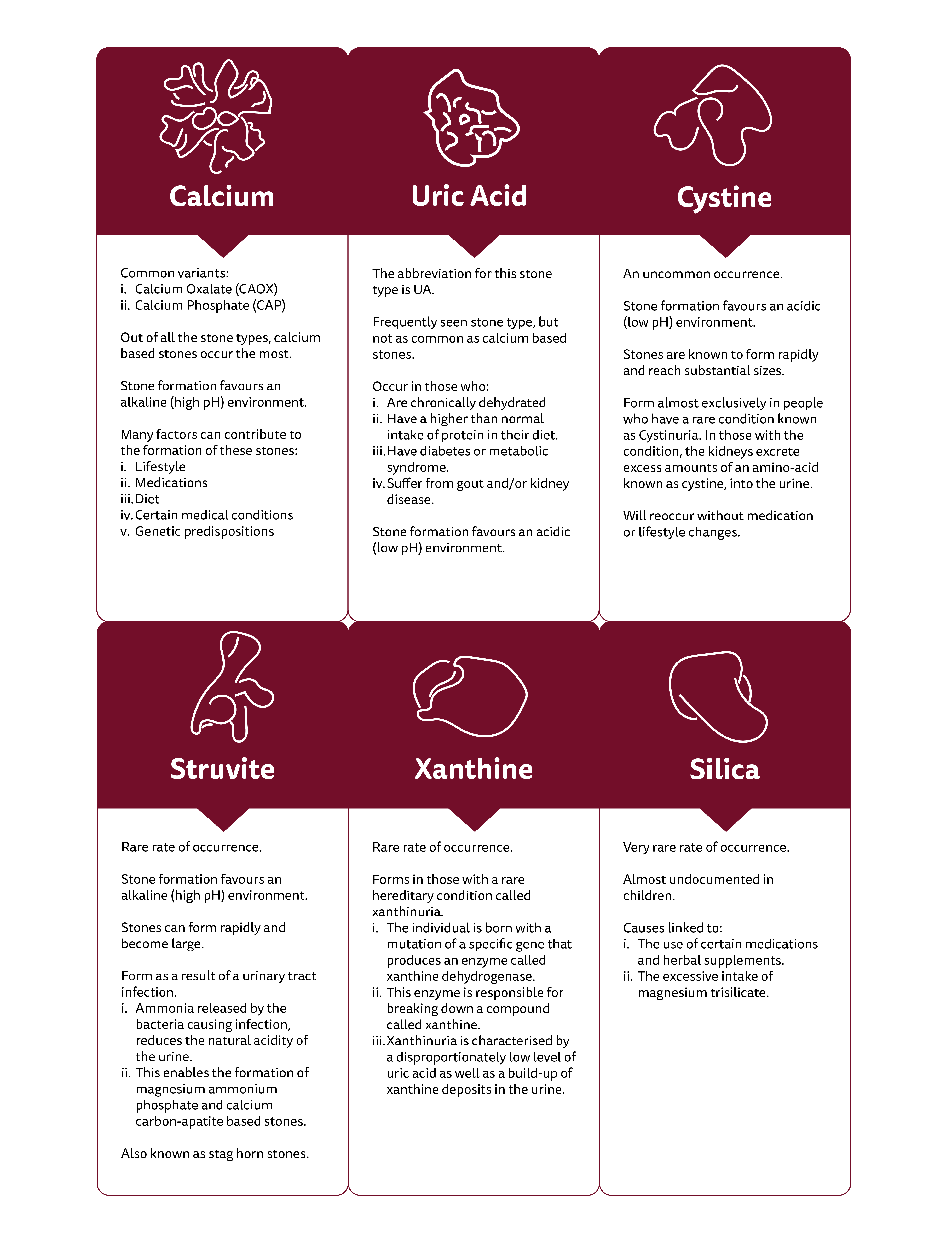
Kidney stones are caused by a plethora of factors that range from diet & lifestyle to hereditary diseases. The appropriate medications and preventative measures will vary depending on the specific type of stone one develops.
There are three main stone types that are encountered the most, being; calcium, uric acid and cystine. Of the three, calcium based stones account for the majority of stone cases. The three less commonly occurring stone types are; struvite, xanthine and silica. Out of those three rarer stone types, silica stones are seen the least.
Prevention
The effort to prevent kidney stones recurring can only begin once your doctor has ascertained the type of kidney stones your body forms. This is done through pathological analysis. Once the kidney stone has been removed or passed by the patient, the stone or its fragments are sent to a lab for analysis. The results of this analysis will inform the doctor how best to treat you going forward.
Treatment and management going forward will almost certainly involve lifestyle & diet changes; your doctor may prescribe medications too should they feel that lifestyle & dietary changes alone, are not enough to prevent a recurrence.
The topic of diet and kidney stone formation was covered in a previous article called, Guide to Kidney Stone Disease & Diet. Give the article a read, should you wish to understand more about how ones diet might be influencing the formation of kidney stones.
pH and Kidney Stones

Certain stone types form in specific urinary pH environments.
Acidic pH:
Uric acid stones
Cystine stones
Alkaline pH:
Calcium stones (Specifically calcium phosphate)
Struvite stones
Depending on the type of stone you form, your doctor may suggest supplements that either acidify or alkalinise the pH of your urine to try prevent the formation of new kidney stones.
Why is it Important to Increase Fluid Intake?
Regardless of stone type or where you are in the process of having a kidney stone, a doctor will tell you the following for free, “Increase your fluid intake!”.
There is a very good reason for this. Inherently, kidney stones form when there is a higher than normal concentration of certain compounds or minerals in the urine.
For example, individuals who inherit the condition known as Cystinuria, lack a specific protein complex found mainly in the kidneys. This protein complex is responsible for reabsorbing certain amino acids, such as cystine, from urine in the kidneys and filtering them back into the blood stream. The lack of this protein complex results in a higher than normal concentration of cystine in the urine, which is where the condition gets its name from, Cystinuria. An environment with higher concentrations of cystine will allow for the formation of cystine based stones. By merely increasing fluid intake (especially if intake is low to begin with), those with Cystinuria can lower their chances of developing cystine stones, as an increased fluid intake will result in more dilute urine that has to be excreted at a higher frequency.
By increasing your fluid intake, stone-formers stand to benefit in the following ways:
- Dilution of the concentration of urine
- Increased urine output
- Increased renal function
- Reduced risk of stone formation
General Measures as per Stone Type
Lifestyle:
- Increase fluid intake
- Reduce oxalate intake (Calcium oxalate formers)
- Reduce sodium intake
- Reduce animal protein intake
Medications:
- Citrate salts
- Thiazide diuretics
- Magnesium (Calcium oxalate formers)
- L-Methionine (Calcium phosphate formers)
Lifestyle:
- Increase fluid intake
- Reduce or eliminate alcohol intake
- Reduce or limit animal protein intake
- Reduce purine intake
Medications:
- Citrate salts
- Allopurinol
Lifestyle:
- Increase fluid intake
- Limit dietary sodium intake
- Reduce alcohol consumption
Medications:
- Citrate salts
- Alkalising agents
Lifestyle:
- Increased fluid intake
- Avoid supplemental magnesium
Medications:
- Antibiotics
- L-Methionine
Lifestyle:
- Increased fluid intake
- Reduce dietary purine intake
Medications:
- Currently, there are no known medications to treat xanthine based stones or xanthinuria
Lifestyle:
- No known lifestyle factors seem to play a role in the formation of silica stones
- Nevertheless, increase fluid intake
Medications:
- If using magnesium trisilicate supplements, stop immediately
- Identify any problem medications and/or supplements and consult your doctor as to whether they might be the cause
Medications
Citrate Salts
Also known as potassium citrate.
Citrate salts bind to compounds in the urine, thus preventing said compounds from binding with one another and forming crystals. Commercially available as soluble tablets, capsules and/or powders.
Citrate salts help to prevent the formation of the following stones:
- Calcium based stones
- Uric acid based stones
- Cystine based stones
Thiazide Diuretics
Thiazide diuretics reduce the amount of calcium that is released into the urine from the bloodstream. Therefore, mitigating the potential for a high concentration of calcium to build up in the urine.
Thiazide diuretics help prevent the formation of the following stones:
- Calcium based stones
Allopurinol
Allopurinols lower the levels of uric acid in the body. The medication achieves this by inhibiting the body from converting purines into uric acid. Purines enter the body through dietary intake; they are abundantly found in certain fish and shellfish, as well as animal meats such as bacon and turkey.
Allopurinol is normally prescribed as a long term treatment for gout. However, the medication also helps to prevent the formation of the following stone types:
- Uric acid based stones
- Calcium oxalate stones
L-Methionine
L-Methionine increases the acidity of ones urine and is prescribed to try prevent the formation of new calcium phosphate stones. Seeing as calcium, specifically phosphate, based stones form in an alkaline environment, by increasing the acidity of the urine the propensity for calcium based stones to form is mitigated.
L-Methionine helps to prevent the following stone types:
- Calcium (specifically phosphate) stones
Antibiotics
Due to their infectious origin, antibiotic treatment is only effective in preventing struvite stone formation.
Modal Box Title
Definitions:
Amino acid: Along with proteins, amino acids are considered the building blocks of life.
In simple terms, amino acids are molecules that combine together to form proteins. Protein that is eaten, gets broken down by the body into amino acids. The resulting amino acids will later combine to form different types of protein that the body needs to function.
Cystine: Cystine is a derivative of the amino acid Cysteine.
In relation to the human body, cystine is found in the following:
- Digestive enzymes
- Cells of the immune system
- In skeletal and connective tissue
- Skin
- Hair
Purine: Chemical compounds found in food that are known to increase uric acid levels and cause gout.
The above article has been compiled using medical research and study outcomes, it is intended to be taken as guidance only. This article should not replace the advice or instruction of a medical practitioner.
Cheers!